Decoding Cholesterol: Understanding the Good, the Bad, and Achieving Optimal Levels
Cholesterol is a crucial substance in our bodies, but its levels and types can significantly impact our health. Let’s explore what cholesterol is, the different types (good and bad), healthy cholesterol levels, variations by age and sex, effective ways to lower cholesterol, dietary recommendations, contributing factors, and more.
- What is Cholesterol?
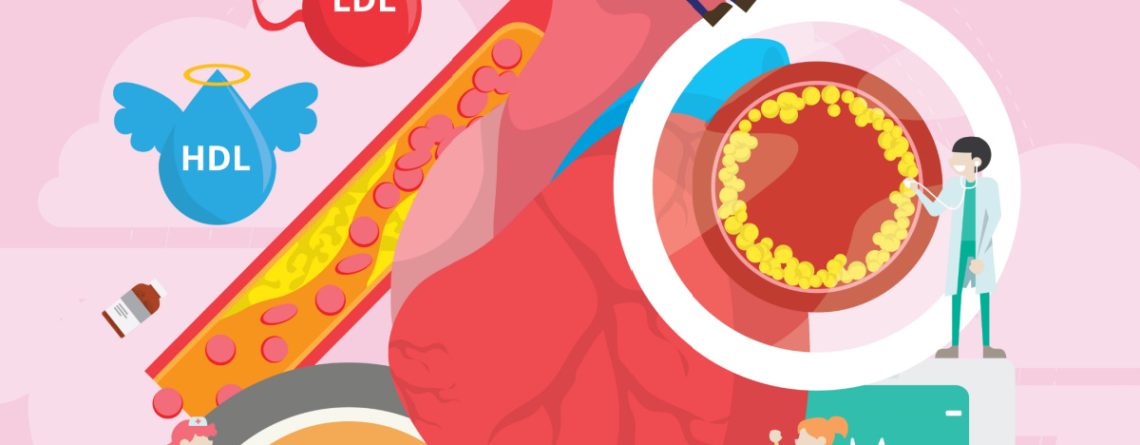
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance produced in our liver and found in certain foods. It plays a vital role in hormone production, cell structure, and digestion. However, excessive cholesterol can pose health risks. - Understanding Good and Bad Cholesterol:
HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol is known as “good” cholesterol because it helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of heart disease. LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, on the other hand, is considered “bad” cholesterol as it can build up in the arteries, leading to blockages and increasing the risk of heart problems. - Healthy Cholesterol Levels:
Ideal cholesterol levels vary based on age and sex. Generally, total cholesterol levels below 200 mg/dL are desirable. HDL cholesterol levels above 40 mg/dL for men and 50 mg/dL for women are considered protective, while LDL cholesterol levels should ideally be below 100 mg/dL. - Cholesterol Levels by Age and Sex:
Cholesterol levels tend to rise with age, and women often have higher HDL cholesterol levels than men. Hormonal changes during menopause can affect cholesterol levels in women. - Lowering Cholesterol:
Lifestyle modifications can help lower cholesterol levels. Regular exercise, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight are essential. Adopting a heart-healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can be beneficial. - Dietary Recommendations:
Reducing saturated and trans fats, limiting dietary cholesterol intake, and incorporating heart-healthy fats like omega-3 fatty acids can help manage cholesterol levels. Foods rich in soluble fiber, such as oats, legumes, and fruits, can also aid in lowering cholesterol. - Contributing Factors:
Several factors influence cholesterol levels, including genetics, obesity, diabetes, and an unhealthy diet. Managing these factors can positively impact cholesterol levels.
Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels is crucial for overall well-being. By understanding the differences between good and bad cholesterol, setting appropriate targets based on age and sex, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, and making dietary adjustments, we can take proactive steps towards optimal cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Note: This article is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance on managing cholesterol levels.