The Power of Protein
Protein, often hailed as the building block of life, is a vital macronutrient essential for various bodily functions. Let’s look into why protein is crucial in the diet, the best ways to consume and absorb it, a breakdown of protein sources, health benefits, and recommendations for protein intake tailored to different age groups and lifestyles.
Why Protein is Essential
Protein plays a crucial role in the body, serving as the foundation for muscles, bones, skin, and tissues. It is composed of amino acids, which are essential for cell repair, growth, and maintenance. Additionally, protein is involved in enzyme production, hormone regulation, and immune function.
Best Ways to Consume and Absorb Protein
- Balanced Meals: Incorporate protein-rich foods into each meal to ensure consistent intake throughout the day.
- Variety: Include a diverse range of protein sources to obtain a wide array of amino acids and nutrients.
- Cooking Methods: Opt for healthier cooking methods like grilling, baking, or steaming to preserve the nutritional content of proteins.
- Timing: Consume protein before and after workouts to support muscle recovery and growth.
- Pairing: Combine protein with carbohydrates and healthy fats to enhance absorption and promote satiety.
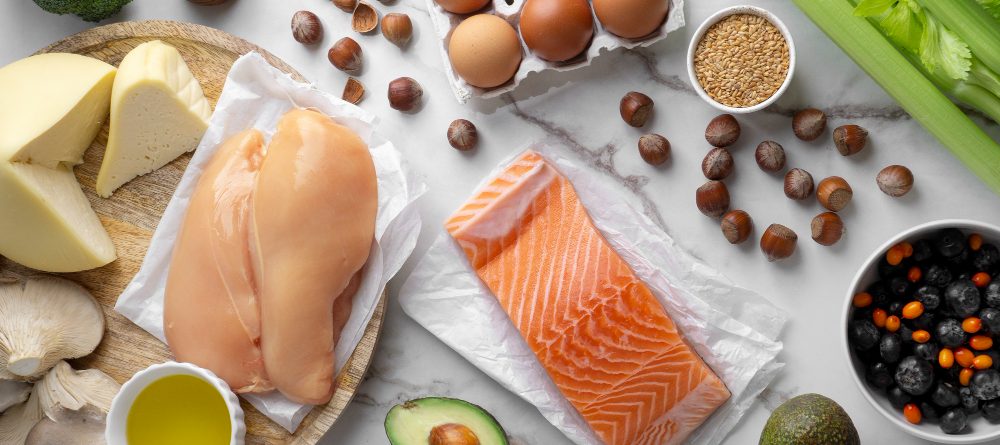
Protein Sources
Meat Options:
- Lean Chicken Breast
- Turkey
- Lean Beef (such as sirloin or tenderloin)
- Pork Tenderloin
- Fish (Salmon, Tuna, Trout)
- Eggs
Vegetable Options:
- Lentils
- Chickpeas
- Black Beans
- Quinoa
- Tofu
- Edamame
- Spinach
- Broccoli
Nut/Seed Options:
- Almonds
- Walnuts
- Chia Seeds
- Pumpkin Seeds
- Hemp Seeds
- Sunflower Seeds
- Peanut Butter
- Cashews
Health Benefits of Protein
- Muscle Growth and Repair: Protein provides the essential amino acids necessary for muscle synthesis and repair, making it essential for athletes and those engaging in resistance training.
- Weight Management: Protein-rich foods promote satiety, reducing hunger and cravings, which can aid in weight loss and weight maintenance.
- Bone Health: Adequate protein intake is associated with improved bone density and reduced risk of osteoporosis.
- Metabolic Health: Protein helps regulate blood sugar levels, insulin sensitivity, and metabolism, potentially reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
- Immune Function: Protein is essential for immune cell production and function, supporting a robust immune system.
Recommended Protein Intake
Age Group: Protein Intake (grams per kilogram of body weight per day)
- Infants (0-6 months): 1.52 g/kg
- Children (1-3 years): 1.05 g/kg
- Children (4-8 years): 0.95 g/kg
- Adolescents (9-13 years): 0.95 g/kg
- Teenagers (14-18 years): 0.85 g/kg
- Adults (19-65 years): 0.8 g/kg
- Older Adults (65+ years): 1.0-1.2 g/kg
***Active individuals, athletes, pregnant or breastfeeding women may require higher protein intake within these ranges.
Protein is an indispensable nutrient that should be prioritized in a balanced diet for optimal health and well-being. By incorporating a variety of protein sources into meals and snacks, individuals can meet their nutritional needs and enjoy the numerous health benefits associated with protein consumption. However, it’s essential to consult healthcare professionals and registered dieticians for personalized dietary recommendations tailored to individual needs and lifestyles. Making informed choices about protein intake can pave the way for a healthier, more vibrant life.