What You Should Know About Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
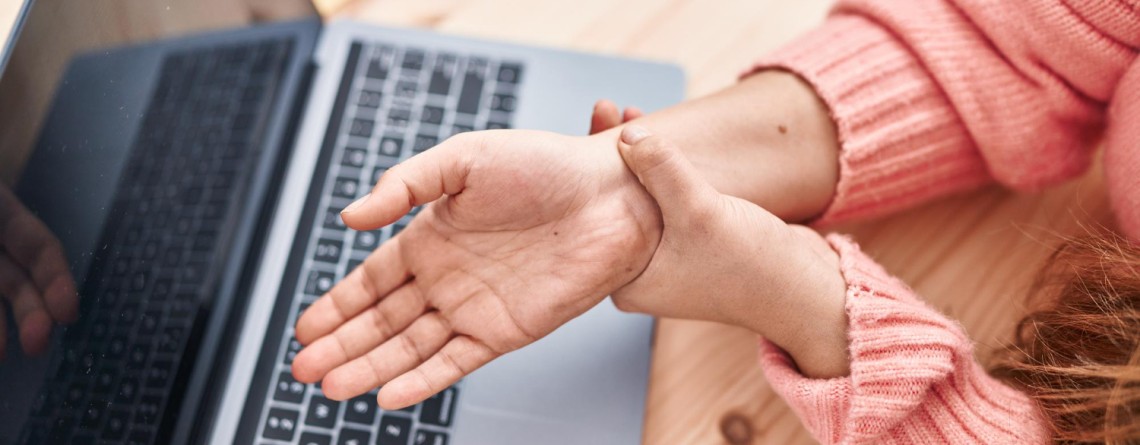
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition characterized by pain, tingling, and numbness in the hand, particularly at the base of the palm. This condition results from compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel, a narrow passage surrounded by bones and ligaments at the wrist. Let’s explore the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for this condition, along with essential preventive measures and dietary recommendations.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The symptoms of CTS typically develop gradually and may worsen over time if left untreated. They include:
- Numbness or tingling in the hand and arm
- Pins and needles sensation
- Pain or discomfort in the wrist and palm
- Hand clumsiness and a tendency to drop things
- Pain at night that may interrupt sleep
- Weakness in the hand and wrist
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of CTS is pressure on the median nerve. Several factors can contribute to this pressure, including:
Anatomic and Medical Factors
- Anatomic factors: Disattachments or arthritis at the wrist can alter the structure of small wrist bones, increasing nerve pressure.
- Nerve-damaging conditions: Diabetes is a significant risk factor.
- Inflammatory conditions: Rheumatoid arthritis can cause swelling and pressure on the nerve.
- Tumors: Lipomas or ganglion cysts that protrude onto the carpal tunnel.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes can cause swelling, compressing the median nerve.
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: A hereditary condition affecting nerves.
Lifestyle and Occupational Factors
- Occupational factors: Jobs that require repetitive hand motions, such as sewing, knitting, carpentry, and baking, increase the risk.
- Obesity and hypothyroidism: Both are associated with an increased likelihood of developing CTS.
- Gender: Women are more commonly affected due to a smaller carpal tunnel structure.
Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
A medical professional typically diagnoses CTS based on symptoms and physical examinations. Diagnostic procedures may include:
- Patient history: Understanding symptoms and possible contributing factors.
- Physical examination: Checking for tenderness, swelling, and nerve response in the hand, neck, shoulder, and elbow.
- X-ray: Used to rule out other causes such as fractures.
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures electrical discharges in muscles to assess nerve function.
Treatment Options
Treatment for CTS depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases often respond to self-care, while severe cases may require medications or surgery.
Medications
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Such as ibuprofen to relieve pain.
- Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and alleviate nerve pressure.
Therapy
- Physical therapy: Stretching exercises to improve hand and wrist function.
Surgical Treatments
- Endoscopic surgery: A minimally invasive procedure guided by a camera to release pressure on the median nerve.
Complications
While CTS does not typically cause complications, surgical treatments can pose risks, including:
- Wound infection
- Scar formation
- Nerve or vascular injuries
Prevention Tips
To reduce the risk of developing CTS, consider the following preventive measures:
- Reduce hand force: Relax your grip when using tools or typing.
- Take frequent breaks: Stretch and bend your hands and wrists periodically.
- Maintain proper posture: Avoid holding your wrist in bent positions.
- Use ergonomic tools: Ensure your computer mouse and workstation setup are comfortable and reduce wrist strain.
Nutritional Recommendations for CTS
Diet can play a role in managing inflammation and nerve health.
Foods to Eat:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish, nuts, and seeds to help reduce inflammation.
- Vitamin-rich foods: Such as cantaloupe and cauliflower for nerve health.
- Anti-inflammatory foods: Include berries and leafy green vegetables.
Foods to Avoid:
- Alcohol: Excessive consumption can worsen nerve health.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
- Which precautions should I take to prevent recurrence?
- Is the condition completely curable?
- What are the best treatment options for my case?
By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, you can take steps to manage or prevent this condition. Making ergonomic adjustments, staying physically active, and maintaining a healthy diet are essential strategies for protecting your hand and wrist health.